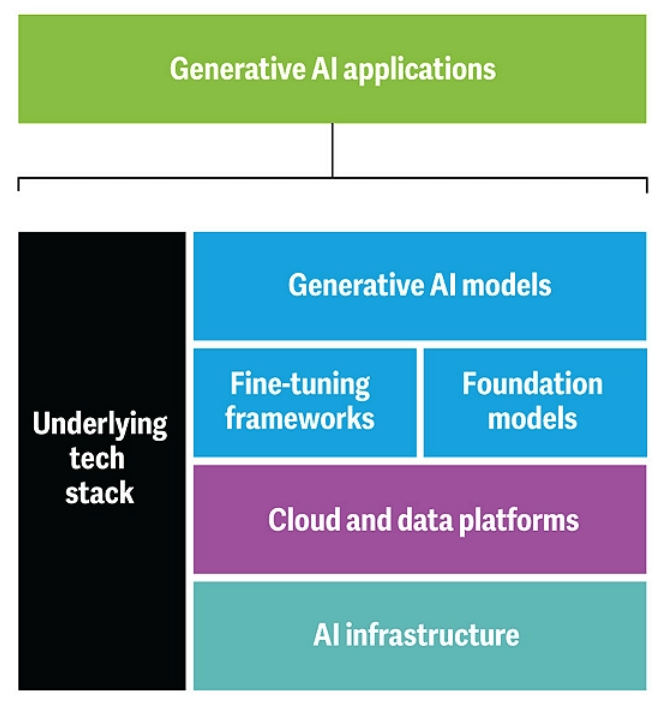
Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems consist of multiple layers extending beyond the visible output. While consumers interact with text, image, video, and audio outputs, these applications are supported by a complex technical stack. This infrastructure includes predictive models, data platforms, and computational resources that enable specialized generative outputs for various tasks and industries.
The architecture of generative AI systems comprises several key components. At the front end, applications provide the interface connecting end-users to trained models. These models, in turn, are supported by fine-tuning and training frameworks that incorporate prompt engineering and adversarial training to enhance model understanding and performance.
Foundation models, such as Large Language Models (LLMs), process vast amounts of data to form the basis of the system’s capabilities.
Underlying these models are cloud and data platforms that store and manage petabytes of information. This data serves as the input for model training and operation. The AI infrastructure, consisting of advanced processing units and scalable systems, provides the necessary computational capacity to train and process these models effectively.
The quality and effectiveness of generative AI applications are directly proportional to the quality and quantity of data used in their development and operation. This underscores the critical importance of robust data management and processing capabilities in the generative AI ecosystem.

Comments by Luis G de la Fuente